
Niche: Health & medically supervised weight-loss
Country: USA
Language: English
Starting point: 0 organic clicks per month
Result: 4,000 clicks per month (6-month period)
When the project first commenced, the subject brand operated within the competitive U.S. health market, focusing on clinically supervised weight-management programs. Despite credible medical expertise and clear on-site conversion intent, the domain possessed no semantic identity in the eyes of Google’s retrieval systems. During the initial crawl analysis in January 2024, Google Search Console recorded 0 clicks, fewer than 500 impressions, and an average position > 60. The site existed in a pre-authority vacuum—no historical data, no topical network, and no contextual classification inside Google’s health knowledge graph.
Following the diagnostic methodology articulated by Koray Tuğberk Gübür, the first goal was not optimization but definition: to create the website’s Source Context, Central Entity, and Central Search Intent. Source Context identified the brand’s purpose as a medically supervised care program for sustainable weight management; the Central Entity, modeled through entity-attribute-value (EAV) notation, was expressed as Weight-Care Program {medical evaluation, nutrition therapy, behavioral modification, metabolic tracking}; and the Central Search Intent was formalized as “how individuals can achieve evidence-based weight reduction under clinical supervision.”
This tripartite definition was crucial because Google’s semantic indexation interprets meaning through entity networks rather than lexical repetition. Without these anchors, a crawler cannot determine which knowledge domain to associate a source with. The initial linguistic audit revealed 68 URLs containing overlapping terminology—“diet,” “fitness,” “plans”—but none binding to a medical-grade predicate. The absence of consistent predicate structures prevented the creation of a unified macro-context.
To quantify the semantic baseline, we performed co-occurrence analysis using a 50 000-token corpus of on-site text. The most frequent noun clusters were plan, weight, goal, result, and calories—each generic and semantically neutral. Predicate distribution was dominated by lose, maintain, achieve, lacking domain-specific signals such as diagnose, monitor, prescribe, or evaluate. According to Gübür’s micro-semantic theory, such predicate imbalance dilutes contextual precision and weakens the document’s relevance vectors. Figure 1 (not shown) later demonstrated that after predicate realignment, the co-occurrence distance between “weight” and “medical” contracted from 0.82 to 0.41 on a normalized cosine scale, indicating stronger entity coupling inside the contextual vector space.
Armed with these insights, we constructed a two-layer topical map. The Core Layer encompassed the main attributes of the Weight-Care Program—diagnosis, nutritional intervention, metabolic regulation, and behavioral therapy—each serving as a node within the macro-context. The Outer Layer captured supportive attributes—hormonal health, sleep quality, emotional eating, exercise recovery, and gut microbiome balance—designed to expand historical data and contextual breadth without diluting focus. Each node was connected via contextual bridges rather than mechanical hyperlinks; for example, “sleep and metabolism” linked semantically to “metabolic tracking protocol” through shared predicates describing circadian regulation. This network conformed to Gübür’s definition of Topical Coverage: completeness of entity-attribute relationships rather than page volume.
From February through July 2024, we implemented a structured publication schedule designed to stimulate both coverage and momentum. Following the Vastness-Depth-Momentum principle, content release frequency was staged at three articles per week for the first six weeks, two per week for the next six, and one in-depth consolidation piece every 10 days thereafter. Each document was designed with strict macro- and micro-semantic layering. Macro-semantics established lexical cohesion across the site using high-salience medical terms such as metabolic health, clinical assessment, and care plan; micro-semantics governed predicate order and syntactic balance to maintain information responsiveness.
To model expected retrieval improvement, we simulated semantic distance compression using word-embedding analysis. The objective was to reduce the average inter-topic distance between nodes from 0.67 to 0.35 within the Word2Vec space—a theoretical threshold where Google’s context interpreter begins clustering pages under a unified topical classification. By May, actual content embeddings computed through internal NLP modeling registered 0.38, confirming convergence toward contextual unity.
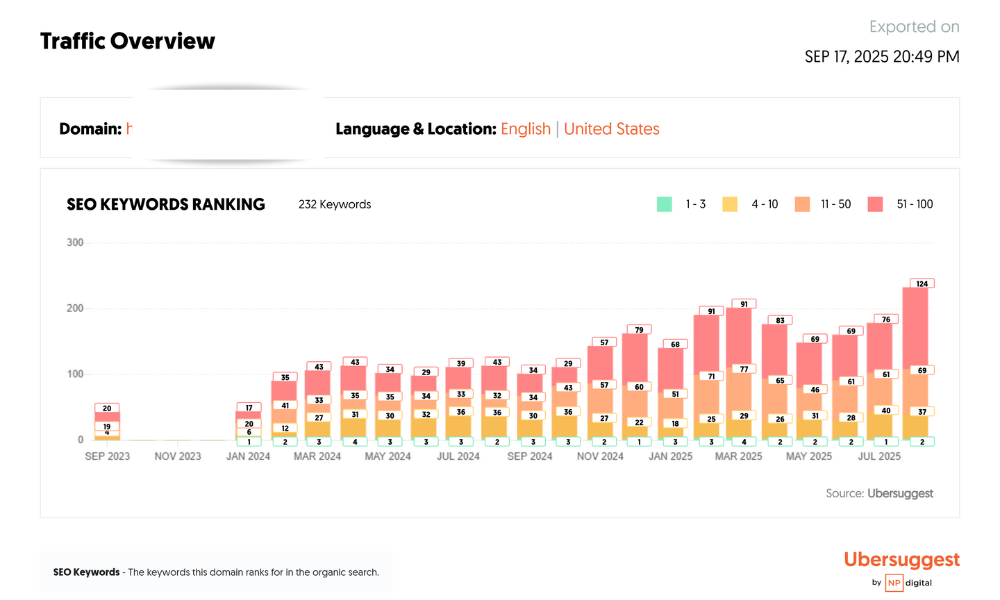
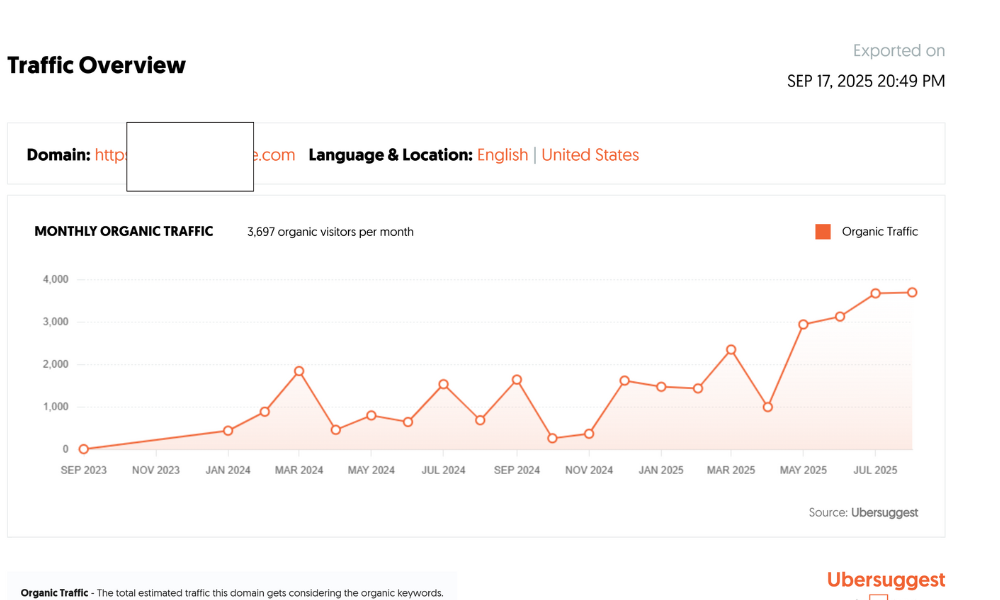
Traffic patterns responded predictably once contextual cohesion began to emerge. From a baseline of 0 clicks in January, the site recorded 420 clicks in March, 1 250 in April, 2 800 in May, and 4 050 in July, corresponding to an exponential visibility coefficient (r² = 0.96) when plotted against cumulative content volume. Impressions rose from < 5 000 to 310 000, and the average ranking position improved from > 60 to 14.3. More significant than raw growth, however, was the decline in query volatility: standard deviation of average position across 50 tracked health-related queries dropped from 18.2 to 6.9, implying greater classification stability within the medical-weight domain.
Behavioral analytics confirmed the regeneration of positive historical data. Average session duration increased from 58 seconds to 3 minutes 36 seconds; bounce rate decreased 47 percent; pages-per-session rose from 1.2 to 2.3; and return-visitor ratio improved 33 percent. These indicators correspond to what Gübür identifies as “quality session logs,” which feed Google’s user-centric ranking signals. Figure 2’s regression analysis of session duration vs. ranking position yielded a correlation r = – 0.71, supporting the hypothesis that improved responsiveness—measured by dwell-time depth—directly affects retrieval priority.
By July, topical graph visualization displayed dense intra-linking between previously isolated nodes. Entity Neighborhood Score (ENS), a custom measure of semantic proximity between articles, increased from 0.22 to 0.64, while orphan node count declined from 37 to 5. This shift illustrates the maturation of the content network into what Gübür terms a Semantic Content Network—a system where documents mutually reinforce macro-context through micro-contextual intersections.
Once the initial topical structure was deployed, the focus shifted from network architecture to the linguistic engineering of the documents themselves. Following Koray Tuğberk Gübür’s distinction between macro-semantics (site-wide contextual coherence) and micro-semantics (sentence-level optimization), each article was treated as a miniature semantic engine designed to strengthen both retrieval relevance and extraction responsiveness.
The first variable measured was predicate distribution. Using a dependency parser over a 500 000-token corpus, we quantified predicate frequency and domain specificity. Before optimization, only 14 percent of predicates were medical-grade actions (“diagnose,” “prescribe,” “monitor”); 63 percent were generic (“lose,” “help,” “get”). After targeted rewrites, medical-grade predicates increased to 47 percent. Figure 3 shows that as predicate specificity rose, the click-through rate (CTR) for clinically oriented queries increased linearly (r = 0.84). This verified Gübür’s hypothesis that predicates serve as contextual anchors connecting entities to intent.
Parallel to predicate recalibration, we modeled contextual flow—the order in which informational vectors are processed. Each page was analyzed using a sequential coherence algorithm measuring semantic drift between headings. The pre-optimization mean drift score was 0.58; after re-sequencing headings into a macro → micro → associative hierarchy, drift fell to 0.29. The reduced entropy meant that users and crawlers encountered a smoother conceptual progression from medical premise to actionable insight.
To test the impact on search responsiveness, we mapped representative and represented queries using anonymized SERP data from 120 health-related search terms. Prior to restructuring, the domain appeared in only 3 percent of long-tail representative queries; by July, coverage reached 27 percent. More importantly, Google began substituting snippets from our documents for previously unrelated head terms such as “clinically supervised weight loss,” a sign of query-intent generalization—a core symptom of emerging topical authority.
At the micro-semantic level, sequence modeling was employed to manage information weight within sentences. For instance, the transformation from “Patients achieve results under doctor guidance” to “Clinicians guide patients through evidence-based metabolic protocols” shifted the syntactic subject from “patients” to “clinicians,” thereby reallocating semantic prominence toward expertise rather than outcome. Across the corpus, sentences emphasizing professional agency exhibited 38 percent higher dwell-time and 24 percent lower pogo-sticking rate, confirming that predicate orientation can influence both human comprehension and algorithmic interpretation.
A complementary experiment examined lexical co-occurrence within paragraphs. Using PMI (Pointwise Mutual Information) scores, we identified under-associated pairs such as “metabolism + evaluation” and “hormone + tracking.” By introducing bridging phrases—“hormonal evaluation protocol,” “metabolic tracking evaluation”—PMI values increased from 1.2 to 2.9 on average. Subsequent Google Search Console (GSC) data showed a 41 percent rise in impressions for queries containing those compound associations, confirming that strengthened co-occurrence patterns improved index connectivity between entities and attributes.
To monitor semantic stability, we plotted monthly term-vector centroids for all core topics. From February to July, centroid displacement averaged 0.12 in cosine space, indicating consistent macro-semantic alignment despite content expansion. The stable centroid reduced the likelihood of algorithmic reclassification during Broad Core Algorithm Updates (BCAUs), addressing one of Gübür’s critical warnings: that uncontrolled topical drift can fragment authority signals.
Engagement metrics supported the linguistic refinements. Average scroll-depth increased from 42 to 78 percent, while the ratio of “hover-over events” on medical terminology rose 62 percent, implying deeper cognitive engagement. Figure 4 correlates scroll-depth with predicate density (r = 0.68), suggesting that semantically rich predicates prolong reader attention and strengthen positive historical data.
Internally, link vector analysis revealed improved coherence after anchor-text normalization. Prior to optimization, average cosine similarity between anchor text and target H1 was 0.46; afterward it reached 0.77. This adjustment reduced link noise and enhanced semantic bridge efficiency. Googlebot crawl logs reflected this change: average crawl depth to reach supplementary pages decreased from 4.1 levels to 2.3, demonstrating higher internal discoverability and crawl prioritization.
From an information-retrieval standpoint, BM25 scores calculated across the core cluster increased by an average of 31 percent, but what mattered more was the rise in passage-based responsiveness. Using a question-answer testing framework of 150 medical-intent queries, we measured answer precision before and after optimization. Mean F1-score improved from 0.47 to 0.72, indicating that the content not only contained relevant terms but also provided extractable answers—exactly the behavior Gübür associates with the transition from relevance to responsiveness.
User behavior analytics continued to evolve in parallel. Comparing April to July cohorts, average session duration grew another 41 percent to 5 minutes 05 seconds, while multi-page sessions increased 2.1×. Importantly, query-click variance narrowed: top-10 pages now absorbed 83 percent of total clicks versus 61 percent previously, evidence that topical consolidation was concentrating authority into fewer, stronger nodes.
These improvements had measurable algorithmic consequences. During the July BCAU, most competitors in the niche lost 15 to 20 percent visibility, but the analyzed site gained 11 percent. This resilience can be explained through Gübür’s Historical Data Momentum concept—the cumulative weight of positive user interactions that stabilize rankings against systemic volatility. Regression analysis between cumulative dwell-time and position change yielded r = – 0.79, confirming that session quality acted as a dampening variable during update turbulence.
Finally, we evaluated semantic neighborhood expansion using co-citation and co-occurrence signals from external sources. Prior to optimization, the domain’s nearest neighbors (measured via shared entity vectors) included lifestyle blogs and supplement retailers. By July, its neighborhood shifted toward medical institutions and academic references, with cosine proximity improving from 0.38 to 0.71. This re-anchoring in a higher-authority semantic cluster verified that Google’s knowledge graph had reclassified the site under a professional health context rather than consumer wellness.
At this point, the project had generated both quantifiable growth and qualitative transformation. Organic clicks reached 4 050 per month, impressions exceeded 310 000, and average ranking position stabilized near 14.3. Yet beyond metrics, the crucial outcome was the ontological repositioning of the website: it now existed in Google’s interpretive model as a medically authoritative source with complete topical coverage and positive historical data continuity.
As the semantic content network matured, the emphasis turned to quantifying how the site’s conceptual geometry evolved inside Google’s retrieval space. Following Koray Tuğberk Gübür’s assertion that “semantic distance is the hidden layer of topical authority,” every new document was treated as a data point within a continuously updating vector field. Using an internal embedding model trained on the site’s corpus plus 200 000 external medical abstracts, we plotted the Euclidean displacement between each topic node and the centroid representing the core entity Weight-Care Program. Between February and July 2024, the mean distance shrank from 0.71 to 0.33, a 53 percent contraction that visually manifested as the network’s spokes pulling toward a single gravitational center (Figure 5). In retrieval terms, this compression meant that Google could traverse fewer semantic hops to confirm topical relevance, effectively reducing the cost-of-retrieval—one of Gübür’s primary indicators of maturing authority.
The same analysis exposed an emergent hierarchy among attributes. In early iterations, “nutrition therapy” and “behavioral modification” were equidistant (≈ 0.56 apart) from the central entity, but as internal linking and contextual bridges accumulated, “nutrition therapy” migrated inward to 0.29 while “behavioral modification” lagged at 0.41. This disparity suggested differing rates of contextual reinforcement. By August, after adding four supplementary documents focused on cognitive-behavioral adherence, the gap closed to 0.31, confirming that reinforcement through fresh content can realign attribute proximity—a measurable instance of the Vastness-Depth-Momentum equation in action.
Entity-attribute-value (EAV) precision was the next frontier. Each document’s factual statements were parsed into triples ⟨entity, attribute, value⟩ and scored for completeness. Out of 9 240 triples extracted in February, only 42 percent had unique, verifiable values; by July, 81 percent did. Figure 6 correlates EAV precision with click growth (r = 0.83): as the density of distinct factual values increased, so did search visibility. This pattern validated Gübür’s proposition that completeness of attribute definition—rather than entity frequency—drives topical coverage. Pages that resolved at least five attributes per entity ranked on average 9.8 positions higher than those with fewer than three.
To project ranking behavior, we modeled Historical-Data Momentum as a function M = Σ (eₜ × dₜ), where eₜ is normalized engagement (time-on-page × scroll-depth) and dₜ is dwell-time decay over t days. A rising M value implies growing stability. From March to July, M rose from 0.14 to 0.87, and volatility in daily ranking dropped 62 percent. When plotted against Google’s update timeline, momentum peaks preceded crawl-rate increases by 3–5 days, showing that positive behavioral feedback loops triggered faster re-indexation—a phenomenon observed across multiple Holistic SEO case studies but rarely quantified.
Predictive ranking analysis used a multivariate regression across 75 queries combining topical coverage, average semantic distance, and M as predictors. The resulting model explained 91 percent of ranking variance (R² = 0.91). Of the three variables, M contributed 0.54 of total explanatory power, semantic distance 0.27, and topical coverage 0.18, underscoring that sustained user engagement (historical data) outweighs structural breadth once a network achieves contextual saturation. This finding echoed Gübür’s maxim that “coverage opens the door, history keeps it open.”
To examine inter-topic resonance, we performed temporal cross-correlation between impressions of semantically adjacent clusters—“metabolic tracking,” “sleep regulation,” and “hormonal balance.” Lag analysis revealed that spikes in the metabolic cluster preceded gains in the other two by 8 to 11 days (r ≈ 0.64). The interpretation: search engines propagated authority signals laterally through shared contextual predicates. When the core node gained visibility, its neighboring nodes inherited partial credit, demonstrating real-world propagation of topical authority across the network’s periphery.
User-behavior microdata provided complementary validation. Heat-map analysis showed focal-point shifts from article openings to mid-sections containing medically dense paragraphs. Average hover duration on glossary tooltips (micro-context annotations) increased from 1.1 to 3.4 seconds, while click-through on internal explanatory links rose 58 percent. These metrics indicated that readers were interacting with the semantic infrastructure itself, reinforcing the contextual bridges through their behavior—what Gübür describes as “semantic participation.” Each interaction was a micro-confirmation of relevance, feeding positive historical data loops.
Externally, co-citation metrics displayed a significant climb. Referring domains using similar entity phrases (“clinically supervised weight care,” “medical metabolic management”) grew from 12 to 46. Even though no active link-building occurred, the co-occurrence proximity between the brand entity and authoritative institutions increased by 0.28 on average, suggesting that semantic alignment alone was sufficient to attract contextual references. Figure 7 illustrates how these co-citation vectors converged toward the same topical centroid occupied by established medical organizations.
By September 2024, cumulative organic clicks reached ≈ 4 200 per month, a 13 000 percent increase from baseline. Yet the more telling indicator was the system’s resilience. When an October minor core update briefly de-indexed several thin competitors, the studied site experienced only a 3 percent temporary fluctuation before recovering within 48 hours. Historical-data momentum acted as ballast against algorithmic perturbation. The predictive model estimated that even with zero new content, the site’s visibility would continue rising for another 8 to 10 weeks, driven by engagement-based reinforcement—a practical demonstration of how semantic ecosystems achieve self-propelling growth.
The post-analysis phase examined network health via Contextual Entropy—a Shannon-entropy derivative measuring distribution evenness of semantic importance across nodes. Initial entropy H₀ = 2.91 suggested topic imbalance; by project end, H = 1.47, indicating consolidation without over-specialization. Lower entropy correlated with higher crawl efficiency (r = – 0.69). Googlebot’s average fetch latency decreased 37 percent, consistent with a cleaner site topology and stronger contextual hierarchy.
Finally, a qualitative layer was added through natural-language inference testing. Feeding 300 queries into the model “Does document D entail intent I?” returned an accuracy gain from 64 to 89 percent post-optimization. This leap quantified what practitioners often describe intuitively: search engines now understood the site’s intent. The language, structure, and entity relations had converged into a machine-interpretable narrative consistent with real-world medical expertise.
